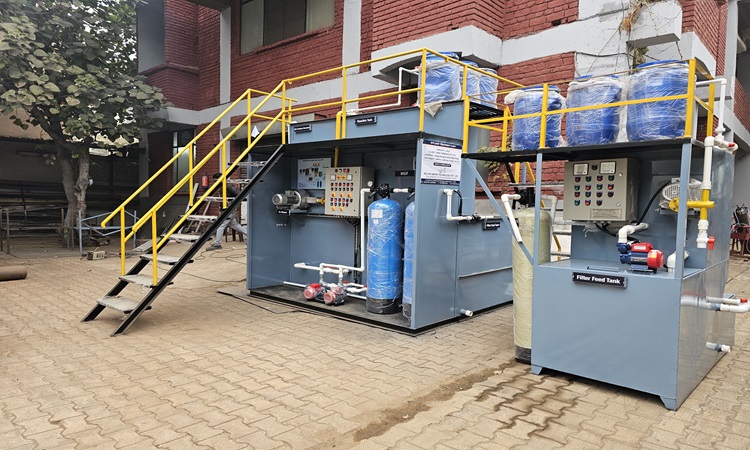
Rapid industrialization has significantly increased the generation of wastewater containing harmful chemicals, oils, heavy metals, and organic pollutants. Managing this industrial effluent responsibly is essential to protect the environment and comply with pollution control regulations. An Effluent Treatment Plant plays a crucial role in treating industrial wastewater and ensuring safe discharge or reuse. This article provides a detailed overview of effluent treatment plants, their working process, technologies, benefits, and future importance.
What Is an Effluent Treatment Plant?
An Effluent Treatment Plant is a system designed to treat wastewater generated from industrial processes. Unlike domestic sewage, industrial effluent often contains complex and toxic substances that cannot be discharged directly into the environment. ETPs use a combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes to remove pollutants and produce treated water that meets regulatory standards.
ETPs are widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, food processing, electroplating, paper, and manufacturing units.
Why Is an Effluent Treatment Plant Important?
Industrial effluent can cause severe environmental damage if left untreated. An efficient effluent treatment plant is essential for several reasons:
- Prevents water pollution
- Protects rivers, groundwater, and soil
- Ensures compliance with CPCB and SPCB norms
- Reduces health hazards
- Promotes sustainable industrial practices
How Does an Effluent Treatment Plant Work?
An effluent treatment plant operates through multiple treatment stages to effectively remove contaminants.
- Preliminary Treatment
This stage involves the removal of large solids, plastics, and debris using bar screens and grit chambers. It protects downstream equipment from clogging and damage.
- Primary Treatment
In primary treatment, wastewater flows into equalization and settling tanks. Suspended solids settle as sludge, while oil and grease are separated using oil skimmers.
- Secondary (Biological) Treatment
This stage removes dissolved and biodegradable organic matter using microorganisms. Common biological treatment methods include:
- Activated Sludge Process (ASP)
- Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
- Tertiary Treatment
Tertiary treatment further polishes the treated water using advanced filtration and disinfection techniques such as:
- Pressure sand filters
- Activated carbon filters
- Reverse osmosis systems
- UV or chlorination
Key Components of an Effluent Treatment Plant
A typical ETP consists of several essential components, including:
- Bar screens and grit chambers
- Equalization tanks
- Chemical dosing systems
- Aeration tanks
- Clarifiers
- Sludge dewatering units
- Filtration and disinfection systems
Types of Effluent Treatment Plants
Effluent treatment plants are designed based on industry type and effluent characteristics. Common types include:
- Chemical effluent treatment plants
- Pharmaceutical ETPs
- Textile and dyeing ETPs
- Food and beverage ETPs
- Electroplating ETPs
Benefits of Installing an Effluent Treatment Plant
Installing an effluent treatment plant offers multiple advantages to industries:
- Compliance with environmental regulations
- Reduced environmental impact
- Water reuse and recycling
- Lower freshwater consumption
- Improved corporate social responsibility
Advanced Technologies Used in Modern ETPs
Modern effluent treatment plants use advanced technologies to improve efficiency and sustainability, including:
- Membrane-based treatment systems
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) integration
- Automation and PLC control panels
- Energy-efficient aeration systems
- Sludge minimization technologies
Operation and Maintenance of ETPs
Proper operation and maintenance are essential for consistent ETP performance. Regular monitoring, chemical optimization, sludge management, and equipment maintenance ensure long-term reliability. Many industries rely on professional ETP service providers for operation and maintenance support.
Role of Kelvin Water Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Kelvin Water Technologies Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted name in the wastewater treatment industry, offering complete effluent treatment plant solutions. The company specializes in ETP design, manufacturing, installation, commissioning, and operation & maintenance services.
Kelvin Water Technologies delivers customized, energy-efficient, and compliance-ready ETP systems for diverse industrial applications. Their expertise in advanced treatment technologies and sustainable solutions makes them a preferred partner for industries across India.
Future of Effluent Treatment Plants
The future of effluent treatment plants lies in:
- Water recycling and reuse
- Zero Liquid Discharge systems
- Smart automation and remote monitoring
- Energy-efficient and compact designs
Conclusion
An Effluent Treatment Plant is an essential component of modern industrial infrastructure. By treating wastewater effectively, ETPs protect the environment, conserve water resources, and ensure regulatory compliance.
With advanced technologies and experienced solution providers like Kelvin Water Technologies Pvt. Ltd., industries can implement efficient, sustainable, and future-ready effluent treatment systems that support long-term growth and environmental responsibility.